How to watch UK TV channels from abroad?
You are traveling outside the United Kingdom or you live outside the United Kingdom, and you do not want to miss out on your favorite TV shows from the United Kingdom. Normally, when you would try accessing UK TV channels on Internet, either through BBC iPlayer, TVplayer or any other website streaming UK centric TV shows over the Internet, you would not be able to access the content on such applications because of geo-restrictions enabled on them. That means, the content on these media streaming applications is accessible only when you are living inside the UK and it blocked when you try to access from anywhere else outside the UK region.
BBC iPlayer is a popular Internet based media streaming service by BBC – British Broadcasting Corporation. BBC iPlayer hosts a number of UK TV shows, movies, music videos, sports events, and more. BBC iPlayers supports media streaming on a number of devices – Smart TV, Laptops, Smartphones, etc.
When a user tries to access BBC iPlayer from countries other than the UK, he’s unable tto view the content due to geo restrictions enabled on it.
Below screenshot shows the error you would get when you normally try and access BBC iPlayer from outside the UK.
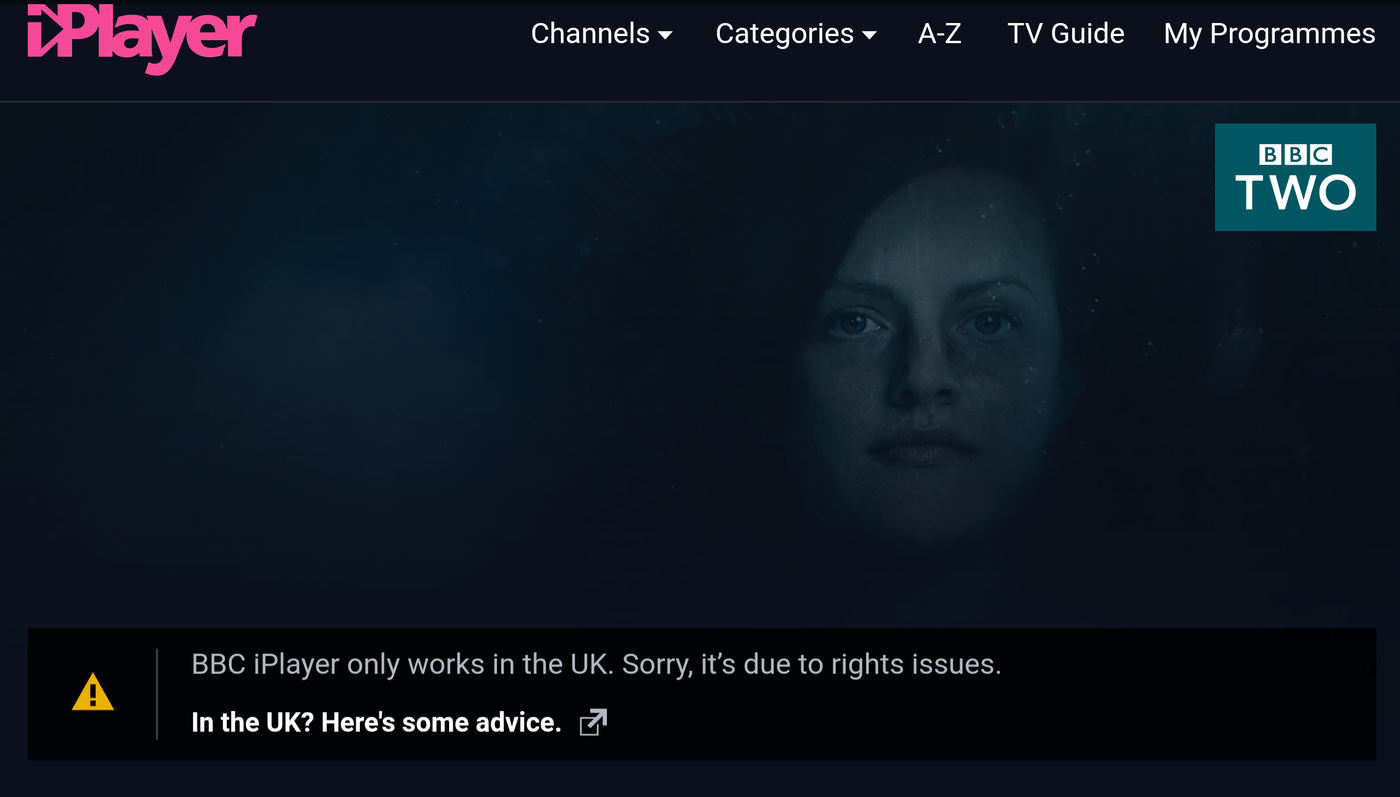
How to unblock and access BBC iPlayer from outside the UK?
There’s a good news for those who would want to watch media content on BBC iPlayer from outside the UK. Here we would explain a method that allows you to bypass geo restrictions and watch your favorite TV shows on BBC iPlayer.
Follow the below simple steps:
1. Get B1-Router
2. Setup B1-Router as per the instructions supplied
3. Connect you Smart TV (or any other device) to B1-Router
4. Login to B1-Router’s Administrative Panel
5. Navigate to Country Gateway tab, select ‘United Kingdom‘ as a country, and confirm it.
6. Wait for a few seconds for the connection status to change and reflect your IP address as a UK based IP address.
7. Visit BBC iPlayer application or website, and watch your favorite TV shows.
B1-Router masks your original IP address and assigns you a UK based IP address, thereby enabling you to access BBC iPlayer easily. B1-Router circumvents the geo restrictions on BBC iPlayer and allows you watch media content on it, outside the UK, from anywhere in the world.
Below screenshot shows BBC iPlayer working outside the UK, unblocked with B1-Router.
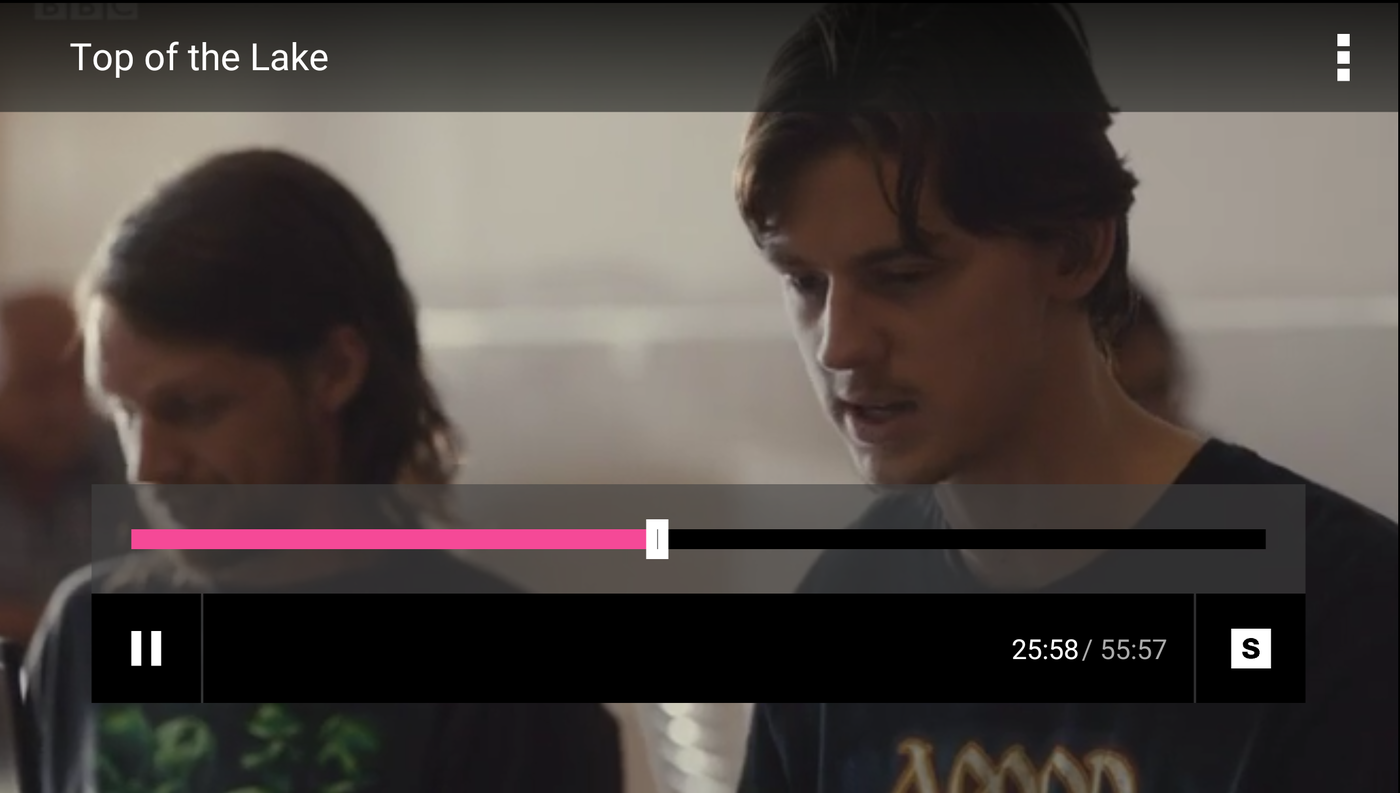
How to unblock TVPlayer outside UK and watch TV channels?
TVPlayer is an Internet-based live TV streaming service for users to watch free-to-air channels through their Smart TV, laptops, smartphones and tablets. The TV service allows television licence holders in the United Kingdom to stream 78 free live television channels, including BBC, ITV, Channel 4, Channel 5, Heart TV, Capital TV and The Box.
TVPlayer offers a “TVPlayer Plus” branded ‘no contract, cancel anytime’ monthly or yearly subscription service which allows consumers access to an additional 30 live streaming television channels, including Gold, Cartoon Network, Discovery Channel, Eurosport 1 and Eurosport 2.
TVPlayer makes it easy for users to watch various TV channels over Internet. However, TVPlayer is only available inside the UK whereas the content on it is blocked when a user is located in any other country outside the UK.
With B1-Router you will also be able to bypass the geo-restrictions on TVPlayer and watch a number of UK based TV channels from anywhere in the world.
Here is what you need to do inorder to access UK TV channels from outside the UK.
Follow the below simple steps:
1. Get B1-Router
2. Setup B1-Router as per the instructions supplied
3. Connect you Smart TV (or any other device) to B1-Router
4. Login to B1-Router’s Administrative Panel
5. Navigate to Country Gateway tab, select ‘United Kingdom‘ as a country, and confirm it.
6. Wait for a few seconds for the connection status to change and reflect your IP address as a UK based IP address.
7. Visit TVPlayer application or website, and watch your favorite TV channels.
B1-Router would unblock TVPlayer for users outside the UK and allow them to watch UK TV channels from anywhere in the world.
TVPlayer blocked outside the UK
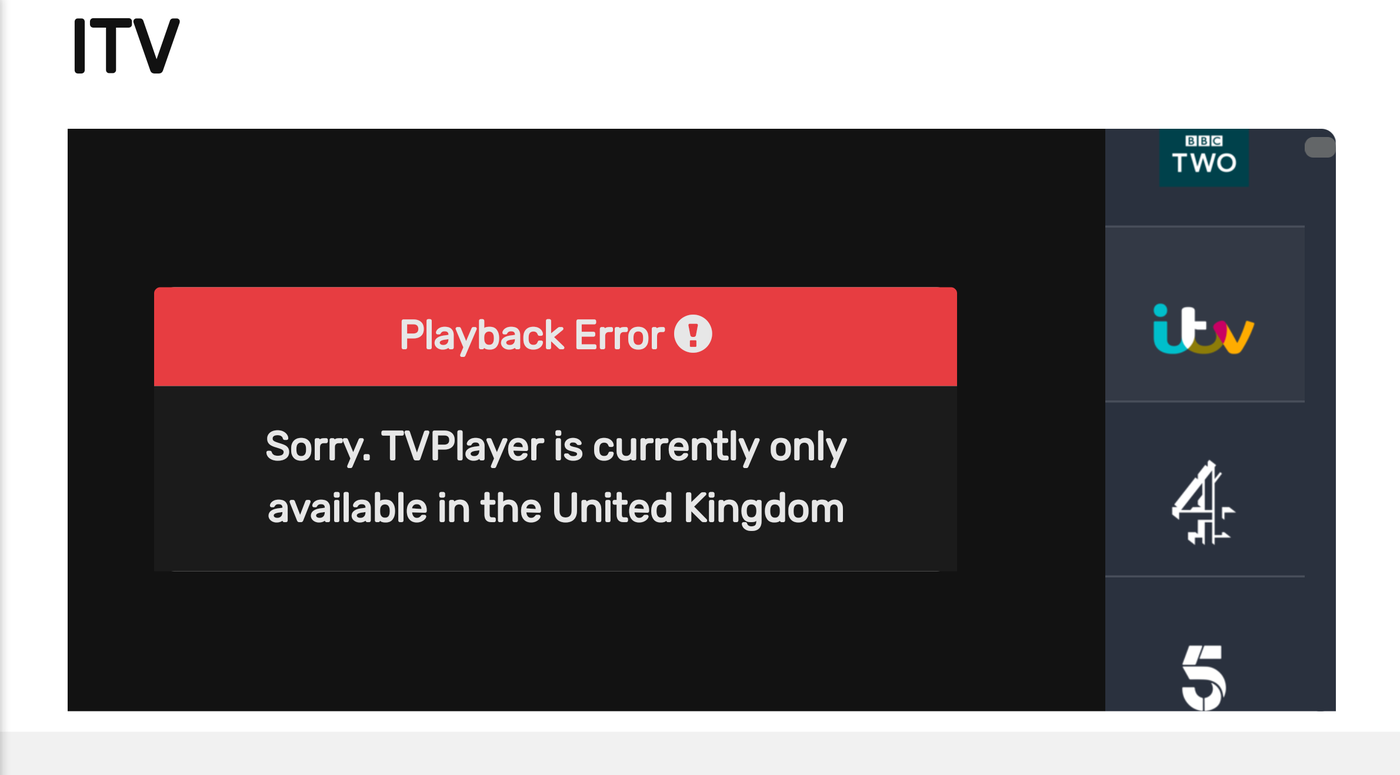
B1-Router masks your original IP address and assigns you a UK based IP address allowing you to watch UK TV channels from anywhere in the world.

For more details about how B1-Router can help watch UK TV channels from abroad, please visit: http://www.b1router.com/en/b1-router-for-uk-tv-channels/
– Captain Krypto
Kryptotel is an IT Security Services and Product Development Company specializing in Cyber Security and Secure Communications. Kryptotel develops secure communication applications with strong encryption and security features. Feel free to consult Kryptotel for your cyber-security challenges. www.kryptotel.net.









